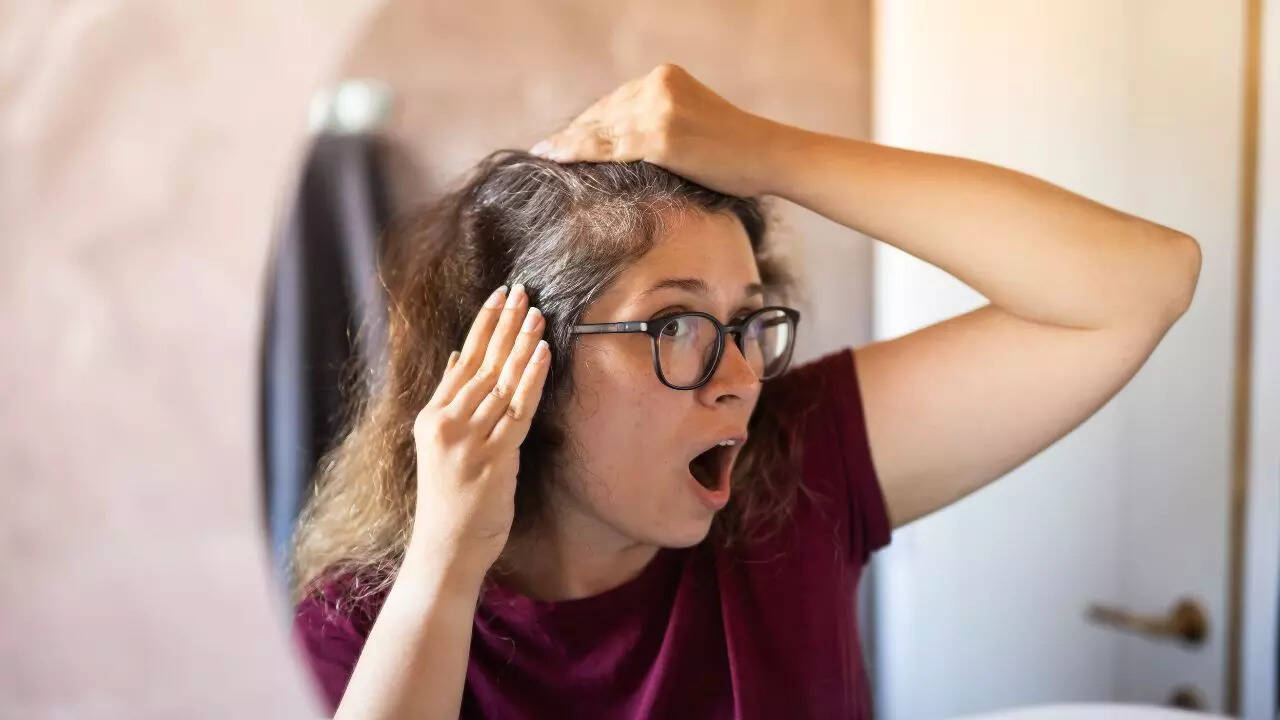
5 foods that may help slow down or prevent premature graying of hair
Folate, or vitamin B₉, may evoke prenatal vitamins more than haircare, but its role in rapidly dividing hair, follicle cells and pigment production is real. A clinical analysis found that individuals with premature graying displayed significantly lower serum folate (6.22 vs. 8.49 ng/mL) compared to non-graying peers. Adults should aim for around 400 µg of Dietary Folate Equivalents (DFE) each day. Foods like beef liver, spinach, and black‐eyed peas offer substantial amounts.
Disclaimer: The information provided is for general educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Dietary changes alone may not prevent or reverse premature graying. Always consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet or addressing hair health concerns.
First Appeared on
Source link