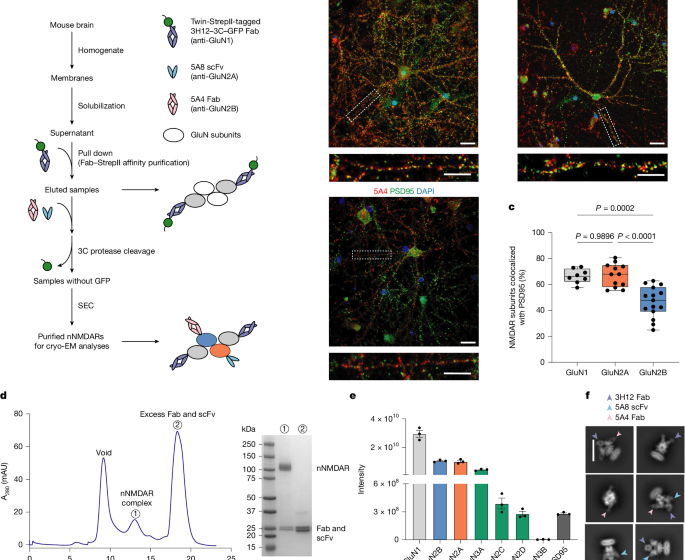
Conformational diversity and fully opening mechanism of native NMDA receptor
Traynelis, S. F. et al. Glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 62, 405–496 (2010).
Lee, C. H. et al. NMDA receptor structures reveal subunit arrangement and pore architecture. Nature 511, 191–197 (2014).
Zhang, M. et al. Assembly and architecture of endogenous NMDA receptors in adult cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Cell 188, 1198–1207 (2025).
Paoletti, P., Bellone, C. & Zhou, Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 383–400 (2013).
Balu, D. T. The NMDA receptor and schizophrenia: from pathophysiology to treatment. Adv. Pharmacol. 76, 351–382 (2016).
McKeage, K. Memantine: a review of its use in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Drugs 23, 881–897 (2009).
Paoletti, P. Molecular basis of NMDA receptor functional diversity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 33, 1351–1365 (2011).
Rauner, C. & Kohr, G. Triheteromeric NR1/NR2A/NR2B receptors constitute the major N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor population in adult hippocampal synapses. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 7558–7566 (2011).
Wyllie, D. J., Livesey, M. R. & Hardingham, G. E. Influence of GluN2 subunit identity on NMDA receptor function. Neuropharmacology 74, 4–17 (2013).
Vicini, S. et al. Functional and pharmacological differences between recombinant N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. J. Neurophysiol. 79, 555–566 (1998).
Erreger, K., Dravid, S. M., Banke, T. G., Wyllie, D. J. & Traynelis, S. F. Subunit-specific gating controls rat NR1/NR2A and NR1/NR2B NMDA channel kinetics and synaptic signalling profiles. J. Physiol. 563, 345–358 (2005).
Gielen, M., Siegler Retchless, B., Mony, L., Johnson, J. W. & Paoletti, P. Mechanism of differential control of NMDA receptor activity by NR2 subunits. Nature 459, 703–707 (2009).
Yuan, H., Hansen, K. B., Vance, K. M., Ogden, K. K. & Traynelis, S. F. Control of NMDA receptor function by the NR2 subunit amino-terminal domain. J. Neurosci. 29, 12045–12058 (2009).
Gielen, M. et al. Structural rearrangements of NR1/NR2A NMDA receptors during allosteric inhibition. Neuron 57, 80–93 (2008).
Jalali-Yazdi, F., Chowdhury, S., Yoshioka, C. & Gouaux, E. Mechanisms for zinc and proton inhibition of the GluN1/GluN2A NMDA receptor. Cell 175, 1520–1532 (2018).
Zhu, S. & Gouaux, E. Structure and symmetry inform gating principles of ionotropic glutamate receptors. Neuropharmacology 112, 11–15 (2017).
Chou, T. H. et al. Molecular mechanism of ligand gating and opening of NMDA receptor. Nature 632, 209–217 (2024).
Goehring, A. et al. Screening and large-scale expression of membrane proteins in mammalian cells for structural studies. Nat. Protoc. 9, 2574–2585 (2014).
Gladding, C. M. & Raymond, L. A. Mechanisms underlying NMDA receptor synaptic/extrasynaptic distribution and function. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 48, 308–320 (2011).
Hardingham, G. E. & Bading, H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 682–696 (2010).
Laurie, D. J. & Seeburg, P. H. Regional and developmental heterogeneity in splicing of the rat brain NMDAR1 mRNA. J. Neurosci. 14, 3180–3194 (1994).
Monyer, H., Burnashev, N., Laurie, D. J., Sakmann, B. & Seeburg, P. H. Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron 12, 529–540 (1994).
Huang, X. et al. Structural insights into the diverse actions of magnesium on NMDA receptors. Neuron 113, 1006–1018 (2025).
Cornelison, G. L. & Mihic, S. J. Contaminating levels of zinc found in commonly-used labware and buffers affect glycine receptor currents. Brain Res. Bull. 100, 1–5 (2014).
Low, C. M., Zheng, F., Lyuboslavsky, P. & Traynelis, S. F. Molecular determinants of coordinated proton and zinc inhibition of N-methyl-d-aspartate NR1/NR2A receptors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11062–11067 (2000).
Paoletti, P., Ascher, P. & Neyton, J. High-affinity zinc inhibition of NMDA NR1–NR2A receptors. J. Neurosci. 17, 5711–5725 (1997).
Zhang, Y. et al. Structural basis of ketamine action on human NMDA receptors. Nature 596, 301–305 (2021).
Zorumski, C. F., Izumi, Y. & Mennerick, S. Ketamine: NMDA receptors and beyond. J. Neurosci. 36, 11158–11164 (2016).
Zhang, J. et al. Distinct structure and gating mechanism in diverse NMDA receptors with GluN2C and GluN2D subunits. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 30, 629–639 (2023).
Esmenjaud, J. B. et al. An inter-dimer allosteric switch controls NMDA receptor activity. EMBO J. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201899894 (2019).
Lu, W., Du, J., Goehring, A. & Gouaux, E. Cryo-EM structures of the triheteromeric NMDA receptor and its allosteric modulation. Science https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal3729 (2017).
Stafford, B. K., Manookin, M. B., Singer, J. H. & Demb, J. B. NMDA and AMPA receptors contribute similarly to temporal processing in mammalian retinal ganglion cells. J. Physiol. 592, 4877–4889 (2014).
Hansen, K. B., Ogden, K. K., Yuan, H. & Traynelis, S. F. Distinct functional and pharmacological properties of triheteromeric GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2B NMDA receptors. Neuron 81, 1084–1096 (2014).
Jones, K. S., VanDongen, H. M. & VanDongen, A. M. The NMDA receptor M3 segment is a conserved transduction element coupling ligand binding to channel opening. J. Neurosci. 22, 2044–2053 (2002).
Yu, J. et al. Mechanism of gating and partial agonist action in the glycine receptor. Cell 184, 957–968 (2021).
Smart, O. S., Goodfellow, J. M. & Wallace, B. A. The pore dimensions of gramicidin A. Biophys. J. 65, 2455–2460 (1993).
Indra, A. K. et al. Temporally-controlled site-specific mutagenesis in the basal layer of the epidermis: comparison of the recombinase activity of the tamoxifen-inducible Cre-ERT and Cre-ERT2 recombinases. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 4324–4327 (1999).
Tyanova, S., Temu, T. & Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 11, 2301–2319 (2016).
Chen, X. et al. Trapped ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry improves the coverage and accuracy of four-dimensional untargeted lipidomics. Anal. Chim. Acta 1210, 339886 (2022).
Punjani, A., Rubinstein, J. L., Fleet, D. J. & Brubaker, M. A. cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 14, 290–296 (2017).
Scheres, S. H. RELION: implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination. J. Struct. Biol. 180, 519–530 (2012).
Punjani, A., Zhang, H. & Fleet, D. J. Non-uniform refinement: adaptive regularization improves single-particle cryo-EM reconstruction. Nat. Methods 17, 1214–1221 (2020).
Goddard, T. D. et al. UCSF ChimeraX: meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Sci. 27, 14–25 (2018).
Jumper, J. et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596, 583–589 (2021).
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004).
Afonine, P. V. et al. Real-space refinement in PHENIX for cryo-EM and crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 74, 531–544 (2018).
Chen, V. B. et al. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 12–21 (2010).
Jain, A., Liu, R., Xiang, Y. K. & Ha, T. Single-molecule pull-down for studying protein interactions. Nat. Protoc. 7, 445–452 (2012).
Hu, X. & Wei, C. RiaXiangzi/Colocalization_ImageJ: Initial release (v1.0.0). Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17922313 (2025).
First Appeared on
Source link