Scientists Discover Hidden Giant Beneath Antarctica’s Ice: A 175-Million-Year-Old Geological Revelation
Beneath the vast, frozen expanse of Antarctica lies a hidden mystery that has puzzled scientists for decades. In a recent study published in Communications Earth & Environment, researchers uncovered an unexpected clue, pink granite boulders scattered across the Hudson Mountains, that led to a remarkable discovery deep below the Pine Island Glacier.
The Discovery of a Hidden Giant Under Antarctica’s Ice
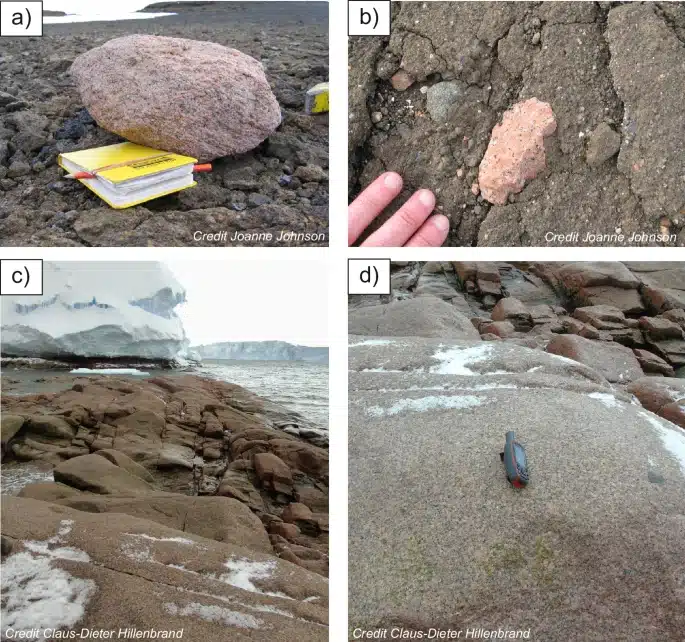
The discovery of a vast granite formation buried deep beneath Antarctica’s Pine Island Glacier has stunned scientists and opened new pathways to understanding the continent’s ice sheet dynamics. For decades, the pink granite boulders scattered across the Hudson Mountains posed a mystery for geologists. The striking color of the rocks, starkly different from the surrounding volcanic landscape, was an anomaly that intrigued researchers but offered little explanation about how the rocks came to rest in such an unlikely place.
Dr. Tom Jordan, the lead author and geophysicist at the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), commented on the significance of the find, stating,
“It’s remarkable that pink granite boulders spotted on the surface have led us to a hidden giant beneath the ice.”
Through a combination of geological dating and gravity surveys, scientists pieced together the history of these ancient rocks, ultimately revealing the presence of a vast granite deposit almost 100 kilometers wide and 7 kilometers thick, lying concealed beneath the glacier. This monumental discovery helps explain the movement and flow of Antarctica’s ice sheet, adding new dimensions to our understanding of the continent’s past and its potential future changes.
Credit:Communications Earth & Environment
Uncovering Clues About the Ice Sheet’s Past
The new findings are not just about uncovering rocks; they offer invaluable clues about the history of the Pine Island Glacier and the ice sheet’s behavior over millions of years. By measuring the radioactive decay within the mineral crystals of the granite, researchers were able to establish that these rocks formed around 175 million years ago, during the Jurassic period. While this alone provided answers about the rocks’ age, it still left the mystery of their current location unanswered.
The breakthrough came when scientists utilized gravity sensors mounted on aircraft to fly over the Pine Island Glacier. The sensors detected an anomaly beneath the ice, hinting at something extraordinary hidden below the surface. As the data was analyzed, the hidden granite deposit was revealed, stretching nearly the size of Wales and buried under layers of ice. Dr. Jordan reflected on the significance of the finding, adding,
“By combining geological dating with gravity surveys, we’ve not only solved a mystery about where these rocks came from, but also uncovered new information about how the ice sheet flowed in the past and how it might change in the future.”

Credit:Communications Earth & Environment
The Role of Granite in Ice Sheet Dynamics
The discovery of the granite formation is more than just an academic curiosity; it has profound implications for understanding how glaciers and ice sheets behave, especially in regions where rapid melting is taking place. The composition of the rocks beneath the ice can influence the movement of the glacier above it. Granite, being a dense and rugged rock, creates friction that can slow down the flow of ice. Conversely, the presence of meltwater channels beneath the glacier can accelerate its movement.
This insight is especially important for regions like the Pine Island Glacier, which is one of the fastest-melting parts of Antarctica. The hidden granite bed beneath it plays a crucial role in how the glacier moves and melts. As Dr. Joanne Johnson, a geologist at BAS and co-author of the study published in Communications Earth & Environment, explained, “Rocks provide an amazing record of how our planet has changed over time, especially how ice has eroded and altered the landscape of Antarctica. Boulders like these are a treasure trove of information about what lies deep beneath the ice sheet, far out of reach.”
Implications for Future Sea-Level Rise Predictions
One of the most pressing issues in contemporary climate science is predicting how Antarctica’s melting ice sheets will affect global sea levels. The Pine Island Glacier, in particular, has been the focus of numerous studies due to its rapid melting. The recent discovery of the granite deposit not only sheds light on the glacier’s past behavior but also offers crucial data that could improve sea-level rise models.
By studying how the glacier has flowed and changed over time, scientists can make more accurate predictions about how it will continue to behave in the future. These models are vital for understanding the potential impact of sea-level rise on coastal populations worldwide. As Dr. Johnson noted, “By identifying their source, we have been able to piece together how they got to where they are today, giving us clues about how the West Antarctic Ice Sheet may change in future – information that is vital for determining the impact of sea level rise on coastal populations around the world.”
First Appeared on
Source link