With food stamps set to dry up Nov. 1, SNAP recipients say they fear what’s next
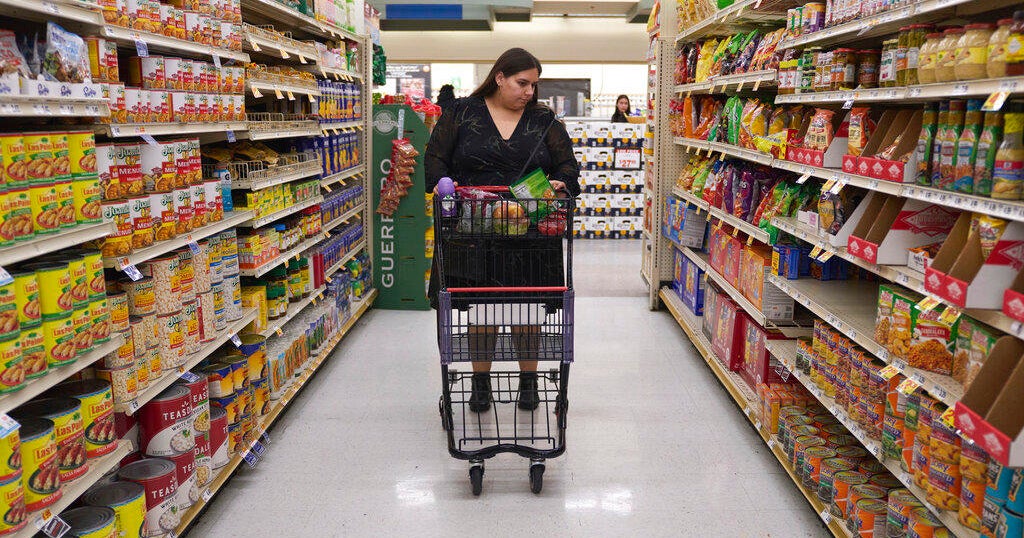
Roughly 42 million Americans rely on food stamps that arrive every month on their electronic benefit transfer cards. On Nov. 1, that aid is set to abruptly stop amid the ongoing U.S. government shutdown, potentially leaving households scrambling to figure out how to put food on the table.
People enrolled in the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, or SNAP, told CBS News they’re bracing for some tough financial choices. Kasey McBlais, a 42-year-old single mom who lives in Buckfield, Maine, said she’s planning to delay paying her electric and credit card bills to make sure her two children have enough to eat.
“Now we’ll have to prioritize which bills we can pay and which can wait,” said McBlais, who works for a Maine social services agency and who draws about $600 a month in SNAP benefits. “My children won’t go hungry.”
The suspension of food aid comes as Democratic and Republican lawmakers continue to trade blame over the government shutdown, which now stands as the second-longest funding lapse in U.S. history. The U.S. Department of Agriculture, which funds the SNAP program, warned earlier this month that there would be insufficient funding to pay full November benefits if the shutdown continued, prompting local governments to post notices on their websites about the potential interruption in payments.
“Bottom line, the well has run dry,” the USDA said in a memo posted Sunday on its website. “At this time, there will be no benefits issued November 01.”
Democratic lawmakers have asked the USDA to use contingency funds to cover most of next month’s SNAP benefits, but an agency memo surfaced on Friday that says “contingency funds are not legally available to cover regular benefits.” The document says the money is reserved for such things as helping people in disaster areas.
That means beginning Nov. 1, the government will halt about $8 billion in monthly SNAP payments, cutting off food assistance for the one in eight Americans who are enrolled in the program. Recipients, who include households in every state, typically get about $187 a month on a prepaid card to help cover the cost of groceries.
Some U.S. states, including Louisiana, Vermont and Virginia, have vowed to continue disbursing SNAP benefits even if the federal government suspends payments. New York on Monday pledged $30 million in emergency food assistance, while also recently committing to provide millions more in support for food banks.
Yet the USDA memo stipulates that states won’t be reimbursed for temporarily providing food aid to residents, raising questions about the viability of that approach.
Sharlene Sutton, a 45-year-old mother of four in Dorchester, Mass., who left her job as a security officer last month to care for one of her children, who has epilepsy, said she relies on the $549 she gets in monthly SNAP benefits to feed her family.
“I was freaking out because I’m like, ‘Oh my god, now I don’t have a job,'” she told CBS News. “I’m not worried about myself that much. It’s about the kids. Like, where am I going to get food from?”
Turning to food banks
Sutton said she’s looking for a food bank to help fill the gap if her food aid is cut off. But experts warn that the non-profit organizations alone aren’t capable of filling the $8 billion monthly hole left by a looming SNAP suspension.
“The charitable food system and food banks don’t have the resources to replace all those food dollars,” John Sayles, CEO of Vermont Foodbank in Barre, Vermont, told CBS News.
Already, food banks are getting an influx of calls from SNAP recipients who are worried about the payments freeze, and food shelves could see long lines next month if the shutdown persists, Sayles said.
“There is no safety net after SNAP other than the food shelf,” he added.
Albuquerque, New Mexico’s Roadrunner Food Bank, which typically serves 83,000 households per week, is “seeing panic” among residents due to the SNAP halt, said Katy Anderson, vice president of strategy, partnerships and advocacy at the nonprofit organization.
Even before this new surge in demand, food banks were already facing pressures because of the growing number of people seeking their services, aggravated this year by persistent inflation, and funding constraints. In March, the USDA said it was nixing $420 million in funding for a program that allows food banks to buy food directly from local farms, ranchers and producers.
A surge in patrons could also strain food banks as they face their own funding struggles and contend with growing demand thanks to inflation ticking higher in March, the USDA said it was nixing $420 million in funding for a program that allows food banks to buy food directly from local farms, ranchers and producers.
Broader economic impact
A temporary halt in $8 billion in monthly food aid could also impact local businesses, from grocers to farm stands, said Sayles of Vermont Foodbank. Each $1 in SNAP benefits provides an economic benefit of $1.60, he said, referring to the so-called multiplier effect in which dollars flowing through the local economy help support spending, jobs and growth.
“SNAP is the foundation of economic support for a lot of food retailers, like those smaller places in rural areas and the corner store in our cities,” said Kate Bauer, an associate professor of nutritional services at the University of Michigan. “So this has far-reaching impacts beyond just the people who get SNAP.”
SNAP is designed to provide supplemental aid for a family’s grocery budget, but some families depend on it as their main source of income to buy food, Bauer noted. For those living paycheck to paycheck, even a short disruption in benefits can have immediate consequences, experts said.
The loss of SNAP funding threatens some of the most vulnerable people in the U.S., with the Center on Budget Policy and Priorities noting that two-thirds of food-stamp recipients are children, seniors or people with disabilities.
For McBlais, the single mom, the issue isn’t political. Rather, it’s about making sure families can eat in an economy where many are already struggling to afford rent, utilities and basic groceries, she told CBS News.
“Everybody needs food — SNAP recipients are Democratic, Republicans and everything in between,” McBlais said.
First Appeared on
Source link